Minimax Search Algorithm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l-hh51ncgDI
- An important search algorithm is the Minimax Algorithm.
- It is a depth-first search algorithm.
- It evaluates the complete tree using the Minimax Algorithm to select the best moves.
Game and Game Playing
If the game tree is sufficiently small, we can generate the entire tree and look ahead to decide which move to make.
- The Minimax algorithm works by generating a complete tree (if possible).
In a two-player game where only one can win, we want to maximize the score for one player (MAX) and minimize the score for the opponent (MIN).
- MAX represents the player trying to win the game by maximizing their score.
- MIN represents the opponent who tries to minimize MAX’s score.
- This assumes that the opponent has and uses the same knowledge of the state space as MAX.
Tree Structure
- Intermediate nodes represent game states.
- Arcs represent moves.
- Leaf nodes hold the score (utility) associated with that path.
Player Turns
- Players alternate moves.
- The first move (layer) may represent MAX.
- The next move represents MIN, and so on.
- Leaf nodes contain utility values.
Evaluation
- Utility values are propagated back up to their parents.
- MAX tries to maximize the minimum values at that position.
- MIN tries to minimize the maximum values at that position.
Each level in the search space contains a label MAX or MIN, indicating whose turn it is at that point in the game.
The Minimax algorithm is used to look ahead and decide which move to make first. It is mainly used in decision-making and game theory.
If the game space is sufficiently small, the entire space can be generated, and leaf nodes can be assigned a win (1), draw (0), or loss (-1) value.
Characteristics of Minimax
- Always finds the optimal path in a finite tree if both players play optimally.
- Struggles with a high branching factor.
- If the game space is large, a game tree can only be generated up to a certain depth (ply).
- Win and loss values cannot be assigned to nodes at the cut-off depth because they are not final nodes.
- Instead, a heuristic value is used.
- Heuristic values estimate how promising a node is for MAX to win.
Minimax Algorithm
Repeat:
If the search limit is reached:
Compute the static value of the current position for the appropriate player.
Report the result.
Otherwise, if it is a minimizing level:
Use Minimax on the children of the current position.
Report the minimum value of the results.
Otherwise, if it is a maximizing level:
Use Minimax on the children of the current position.
Report the maximum value of the results.
Until the entire tree is traversed.
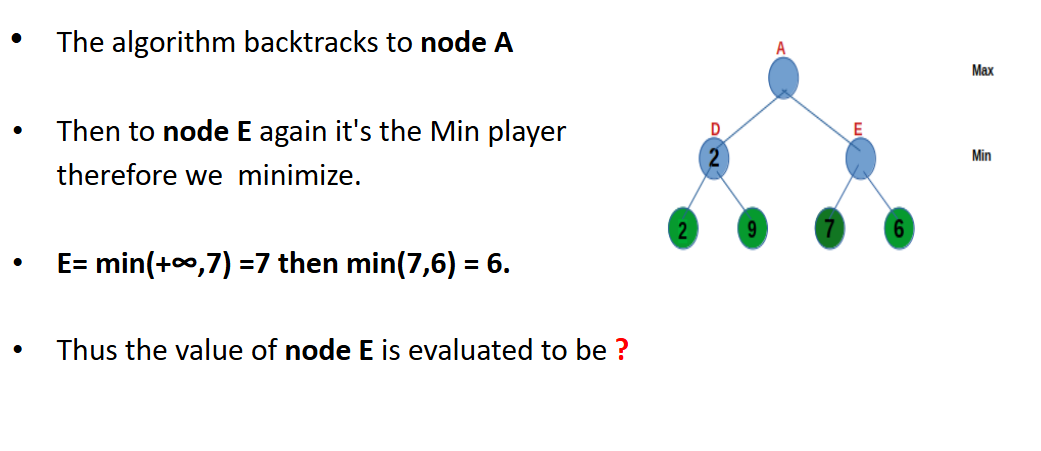
Example
Advantages
- Considers all possible moves.
- Ensures optimal moves are made.
- Highly accurate in finding the best move.
Drawbacks
- For complex games (e.g., chess) with a large branching factor, it is very slow.
Solution:
[Alpha-Beta Pruning] can be used to improve efficiency.