Alpha Beta Pruning
The disadvantage of the minimax algorithm is that all nodes in the game tree cut off to a certain depth were examined.
Alpha-beta pruning reduces the number of nodes explored.
Key Points
- Game trees can be enormous.
- Some branches have no effect.
- Several branches can be removed.
- Pruning the branches reduces the time for the minimax algorithm.
Alpha & Beta Variables
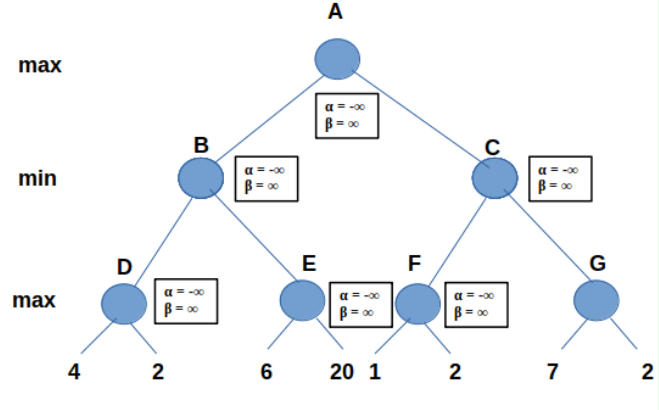
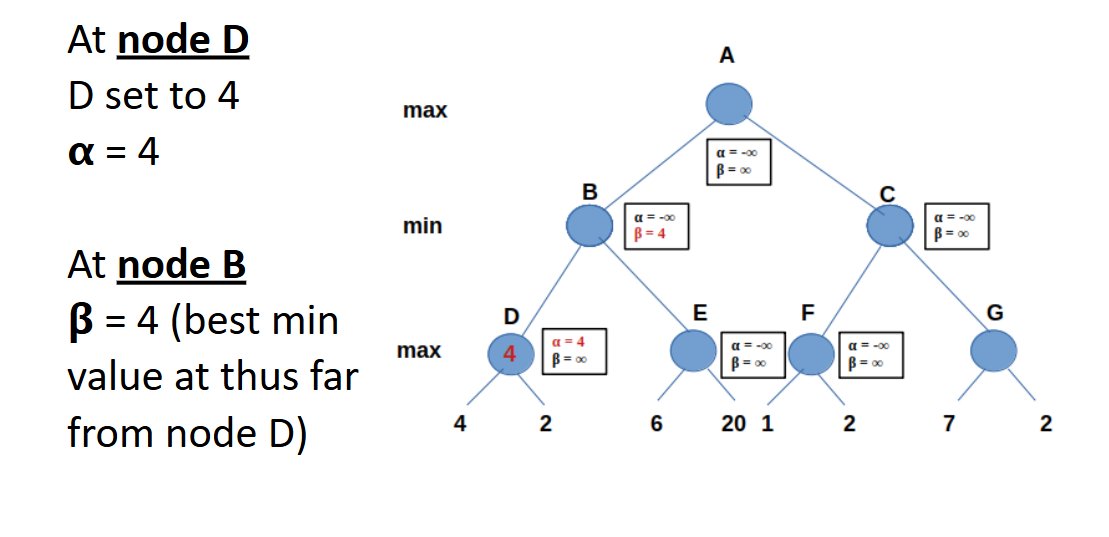
Two extra variables are assigned to every node in the tree: alpha (α) and beta (β).
ALPHA (α)
- Stores the best already explored option along a path to the root for the max layer.
- Represents the maximum score the maximizer can receive.
- Only the maximizer can change this value.
- Initial value: -∞ (negative infinity).
BETA (β)
- Stores the best already explored option along a path to the root for the minimizing layer.
- Represents the minimum score the maximizer can receive.
- Only the minimizer can change this value.
- Initial value: ∞ (positive infinity).
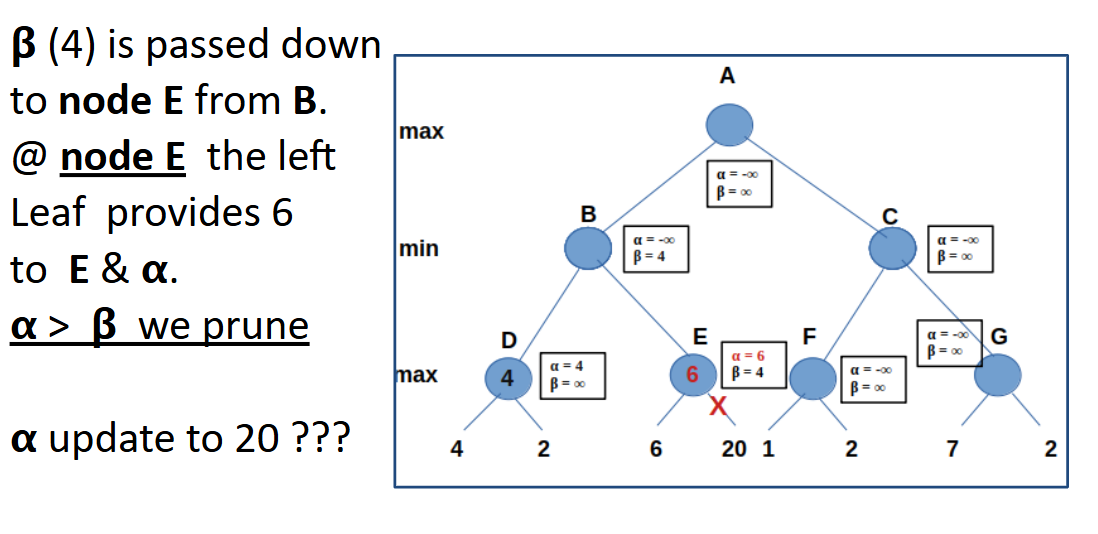
Pruning Condition
- If α ≥ β, a given branch can be pruned, meaning there is no need to visit the given children.
- Pruning is not always guaranteed—it depends on the distribution order of values.
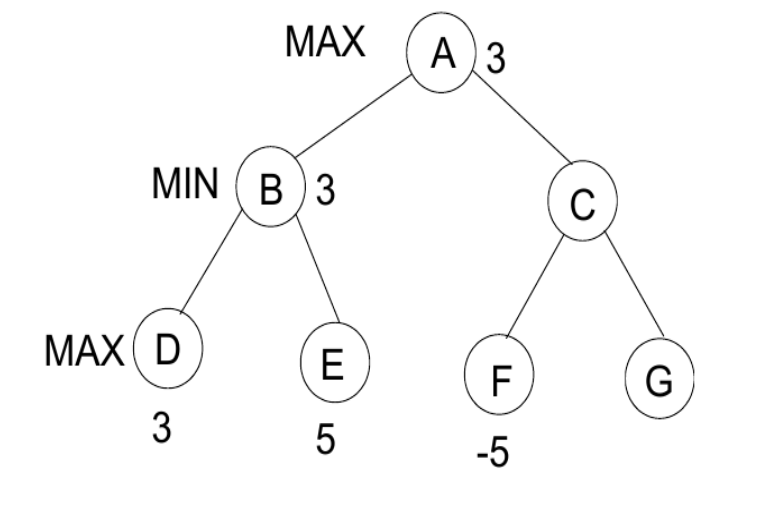
Sample 1
The children of B have static values of 3 and 5, and B is at the MIN level, so the value returned to B is 3.
If we consider F, it has a value of -5.
Thus, the value returned to C is at most -5. However, A is at a MAX level, meaning the value at A will be at least 3, which is greater than -5.
Regardless of the value of G, A has a value of 3. Therefore, we do not need to explore G because its value will not affect the value returned to A.
This is called the alpha cut.
Similarly, we can get a beta cut if the value of a subtree is always greater than the value returned by its sibling at a minimizing level.
In Alpha-Beta pruning, we assign two extra variables to every node in the search tree: alpha (α) and beta (β).